Table of contents
Adaptive Bitrate playback
Encoding and packaging the media content with multiple bitrates and resolutions enables adaptive media streaming. Mediaplayers such as dash.js can dynamically switch between different bitrates and resolutions based on factors such as the current throughput, the current buffer level and the resolution on the end device.
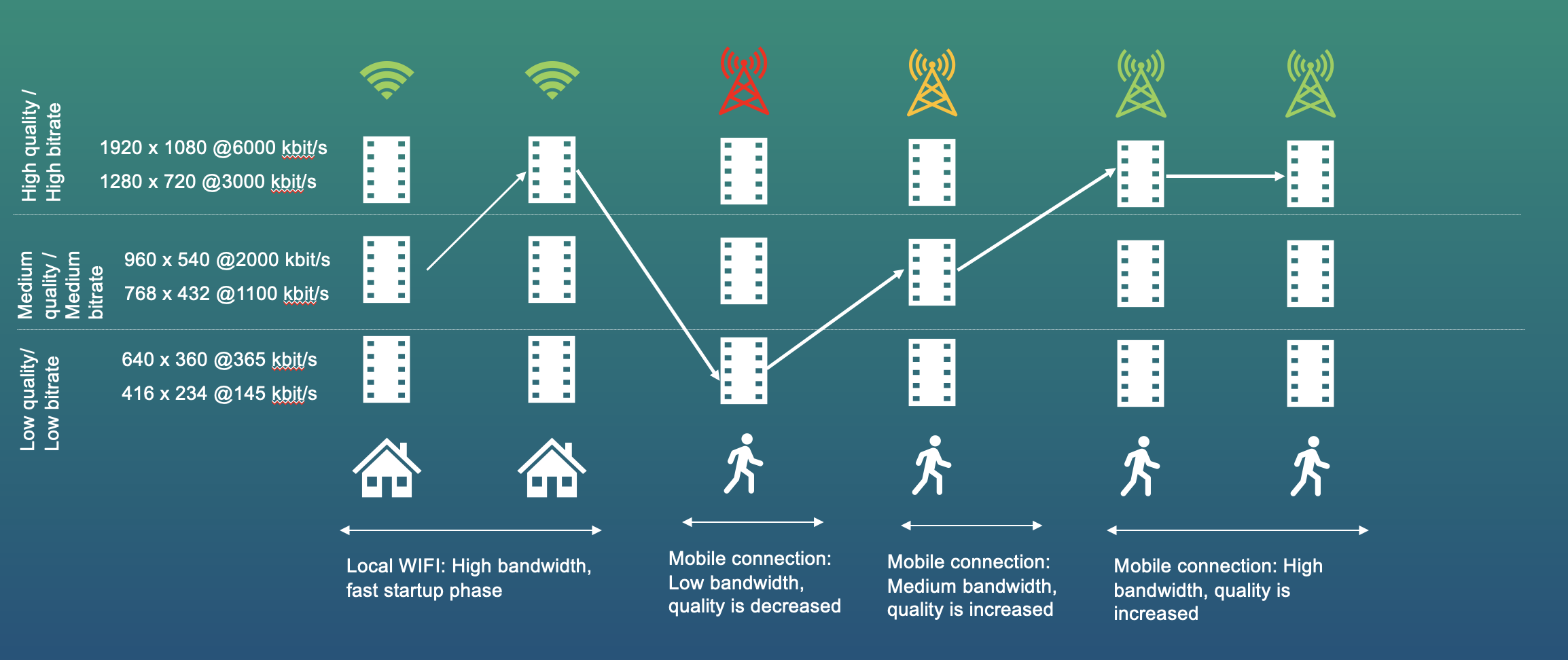
dash.js has a flexible ABR decision logic in place that can be dynamically adjusted and extended. In the following we describe the various settings that dash.js offers and how to plug in your own ABR algorithm.
ABR Examples
Multiple samples implementing the functionalities described in this documentation can be found in the ABR section.
Changing the default ABR algorithm
dash.js ships with predefined ABR rules. Per default, dash.js combines a throughput based ABR rule with a buffer based ABR rule (abrDynamic). The abr section in Settings.js allows a reconfiguration of the default ABR algorithm:
player.updateSettings({
streaming: {
abr: {
ABRStrategy: 'abrDynamic'
}
}
});
| ABR Rule | Description |
|---|---|
abrDynamic | Dynamically switch between the throughput rule and the buffer rule |
abrThroughput | Use the throughput rule. |
abrBola | Use the BOLA buffer based rule. |
A detailed example is available here.
Additional ABR rules
Next to the main ABR rules described above, dash.js defines additional ABR rules that run alongside the main rules and can be dynamically enabled and disabled.
player.updateSettings({
streaming: {
abr: {
additionalAbrRules: {
insufficientBufferRule: true,
switchHistoryRule: true,
droppedFramesRule: true,
abandonRequestsRule: true
}
}
}
});
| ABR Rule | Description |
|---|---|
insufficientBufferRule | tbd |
switchHistoryRule | tbd |
droppedFramesRule | tbd |
abandonRequestsRule | tbd |
A detailed example is available here.
Adding a custom ABR rule
dash.js allows applications to define their own ABR algorithms. For that reason, disable the default ABR rules and use addABRCustomRule to add your new rule:
var video,
player,
url = "https://dash.akamaized.net/akamai/bbb_30fps/bbb_30fps.mpd";
video = document.querySelector("video");
player = dashjs.MediaPlayer().create();
/* don't use dash.js default rules */
player.updateSettings({
'streaming': {
'abr': {
'useDefaultABRRules': false
}
}
});
/* add my custom quality switch rule. Look at LowestBitrateRule.js to know more */
/* about the structure of a custom rule */
player.addABRCustomRule('qualitySwitchRules', 'LowestBitrateRule', LowestBitrateRule);
player.initialize(video, url, true);
A detailed example is available here.
Disabling the ABR behavior
dash.js allows applications to disable the adaptive bitrate behavior. For that reason, simply disable the autoSwitchBitrate setting for the respective media type:
var video,
player,
url = "https://dash.akamaized.net/akamai/bbb_30fps/bbb_30fps.mpd";
video = document.querySelector("video");
player = dashjs.MediaPlayer().create();
player.updateSettings({
streaming: {
abr: {
autoSwitchBitrate: {audio: true, video: false},
}
}
});
player.initialize(video, url, true);
A detailed example is available here.
Selecting the initial bitrate
In some cases the application wants to define the initial bitrate for either the audio track or the video track prior to the start of the stream. For that reason, simply use the initialBitrate setting. The target value is specified in kbps. In the example below the initial bitrate for video is set to 800 kbit/s.
function init() {
var video,
player,
url = "https://dash.akamaized.net/akamai/bbb_30fps/bbb_30fps.mpd";
video = document.querySelector("video");
player = dashjs.MediaPlayer().create();
player.updateSettings({
streaming: {
abr: {
initialBitrate: {audio: -1, video: 800}
}
}
});
player.initialize(video, url, true);
}
A detailed example is available here.
Defining a minium/maximum bitrate
In some cases you might want to define a minimum and/or a maximum bitrate. dash.js will then only adapt the bitrate within these thresholds. In the example below the maximum bitrate for video is set to 5000 kbit/s while the minimum bitrate for video is defined as 2000 kbit/s.
var video,
player,
url = "https://dash.akamaized.net/akamai/bbb_30fps/bbb_30fps.mpd";
video = document.querySelector("video");
player = dashjs.MediaPlayer().create();
player.updateSettings({
streaming: {
abr: {
maxBitrate: {audio: -1, video: 5000},
minBitrate: {audio: -1, video: 2000},
}
}
});
player.initialize(video, url, true);
A detailed example is available here.
Fast bitrate switching
When the quality/bitrate for a certain media type is changed dash.js has two options. It can either append the next fragment at the end of the current buffer or replace existing parts of the buffer with the newly selected quality.
When fastSwitchEnabled is set to true the next fragment is requested and appended close to the current playback time. Note: When ABR down-switch is detected, we append the lower quality at the end of the buffer range to preserve the higher quality media for as long as possible.
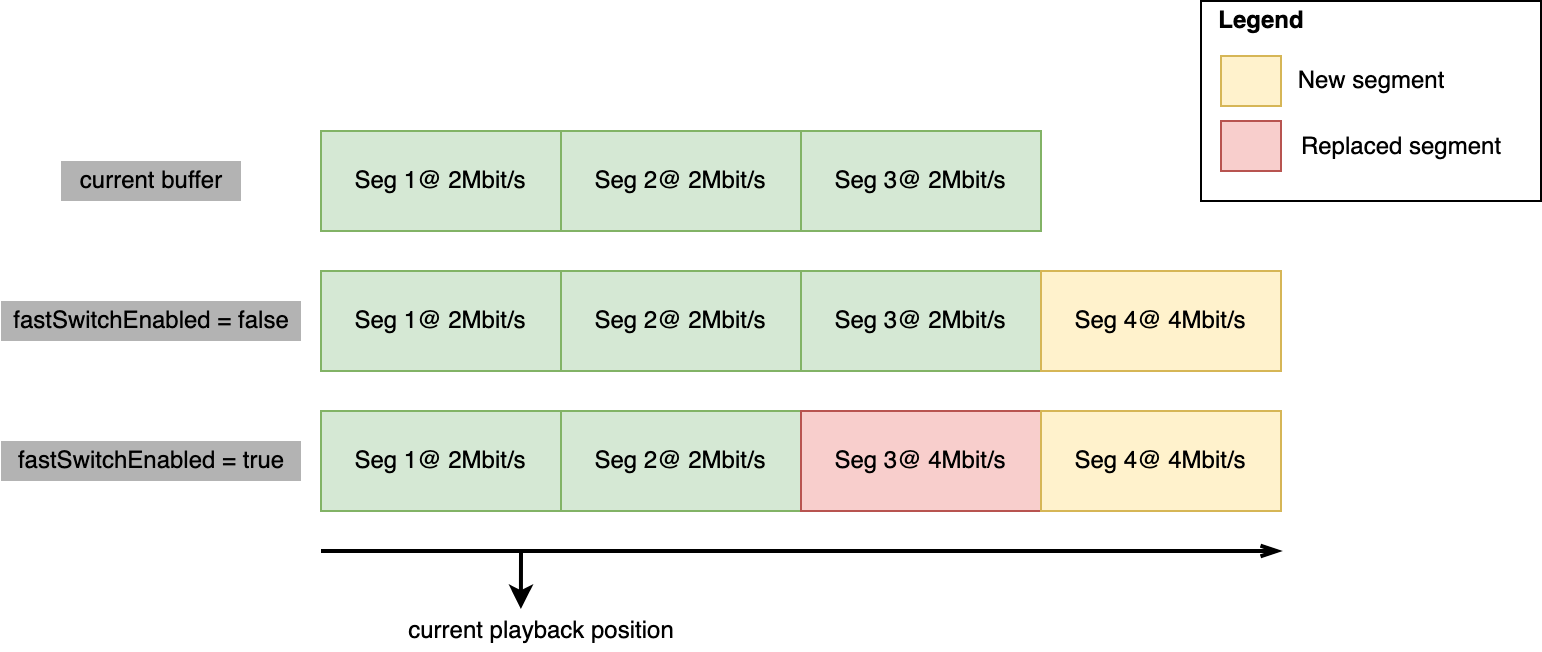
var video,
player,
url = "https://dash.akamaized.net/akamai/bbb_30fps/bbb_30fps.mpd";
video = document.querySelector("video");
player = dashjs.MediaPlayer().create();
player.updateSettings({
streaming: {
buffer: {
fastSwitchEnabled: true
}
}
});
player.initialize(video, url, true);
A detailed example is available here.